
Losana McGowan

El Consejo de Derechos Humanos (CDH) es el cuerpo intergubernamental del sistema de las Naciones Unidas responsable de la promoción y protección de todos los derechos humanos en todo el mundo. El HRC se reúne en sesión ordinaria tres veces al año, en marzo, junio y septiembre. La La Oficina del Alto Comisionado para los Derechos Humanos (ACNUDH) es la secretaría del Consejo de Derechos Humanos.
Debate y aprueba resoluciones sobre cuestiones mundiales de derechos humanos y el estado de los derechos humanos en determinados países
Examina las denuncias de víctimas de violaciones a los derechos humanos o las de organizaciones activistas, quienes interponen estas denuncias representando a lxs víctimas.
Nombra a expertos independientes que ejecutarán los «Procedimientos Especiales» revisando y presentado informes sobre las violaciones a los derechos humanos desde una perspectiva temática o en relación a un país específico
Participa en discusiones con expertos y gobiernos respecto a cuestiones de derechos humanos.
A través del Examen Periódico Universal, cada cuatro años y medio, se evalúan los expedientes de derechos humanos de todos los Estados Miembro de las Naciones Unidas
Se está llevarando a cabo en Ginebra, Suiza del 30 de junio al 17 de julio de 2020.
AWID trabaja con socios feministas, progresistas y de derechos humanos para compartir conocimientos clave, convocar diálogos y eventos de la sociedad civil, e influir en las negociaciones y los resultados de la sesión.

Feminist movements have changed and adapted tremendously since we last convened in this way - so to remember why AWID Forums matter, we asked activists from around the world to reflect on and share their stories, impressions and memories. This is what we learned.
Esta película cuenta la historia de un hombre misterioso cuya vida ha sido moldeada por la huida, la expulsión, el exilio y el fracasado retorno a Palestina. El film está compuesto por la búsqueda de respuestas que lleva a cabo su hija.

By: Marianne Mesfin Asfaw

I have many fond memories in my journey with feminism, but one in particular that stands out. It was during my time at graduate school, at a lecture I attended as part of a Feminist Theory course. This lecture was on African feminism and in it the professor talked about the history of Pan Africanism and the ways in which it was patriarchal, male-centric, and how Pan Africanist scholars perpetuated the erasure of African women. She talked about how African women’s contributions to the anti-colonial and decolonial struggles on the continent are rarely, if ever, discussed and given their due credit. We read about the African feminist scholars challenging this erasure and actively unearthing these stories of African women led movements and resistance efforts. It seems so simple but what stood out to me the most was that somebody put the words African and feminist together. Better yet, that there were many more of us out there wrestling with the complicated history, politics and societal norms in the various corners of the continent and we were all using a feminist lens to do this. I came out of that lecture feeling moved and completely mind-blown. After the lecture three of my friends (all African feminists) and I spent some time debriefing outside the classroom. We were all so struck by the brilliance of the lecture and the content but, more than anything, we all felt so seen. That feeling stood out to me.
Falling in love feminism was thrilling. It felt like finally getting to talk to your longtime crush and finding out that they like you back. I call it my crush because in high school I referred to myself as a feminist but I didn’t feel like I knew enough about it. Was there a right way to be feminist? What if I wasn’t doing it right? Attending my first Women’s Studies lecture answered some of these questions for me. It was thrilling to learn about stories of feminist resistance and dismantling the patriarchy. I felt so affirmed and validated, but I also felt like something was missing.
Deepening my relationship with feminism through academia, at an institution where the students and teaching staff were mostly white meant that, for those first few years, I noticed that we rarely had discussions about how race and anti-blackness show up in mainstream feminist movements. In most courses we had maybe 1 week, or worse 1 lecture, dedicated to race and we would usually read something by bell hooks, Kimberly Crenshaw’s work on intersectionality, and maybe Patricia Hill Collins. The following week we were back to sidelining the topic. I dealt with this by centring race and black feminism in almost all my assignments, by writing about black hair and respectability politics, the hypersexualization of black women’s bodies, and so much more. Over time I realized that I was trying to fill a gap but didn’t quite know what it was.
Encountering and learning about African feminism was a full circle moment. I realized that there was so much more I had to learn.
Mainly that my Africanness and my feminist politics did not have to be separate. In fact, there was so much that they could learn from each other and there were African feminists out there already doing this work. It was the missing piece that felt so elusive during my exploration of feminism throughout my academic journey.
Feminism to me is the antithesis to social and political apathy. It also means once you adopt a feminist lens, nothing can ever be the same. My friends and I used to talk about how it was like putting on glasses that you can never take off because you now see the world for what it is, mess and all. A mess you can’t simply ignore or walk away from. Therefore my vow to the feminist movement is to never stop learning, to keep stretching the bounds of my empathy and to never live passively. To dedicate more time and space in my life to feminist movements and to continue to amplify, celebrate, document and cite the work of African feminists. I also commit to centring care and prioritizing pleasure in this feminist journey because we can’t sustain our movements without this.

Be it core funding, programmes & projects or rapid response/ emergency grants.
Aïssata Kane, surnommée affectueusement “Yaye Kadia” (Mère Kadia), a de tout temps été une féministe engagée dans la défense des droits des femmes africaines, et particulièrement mauritaniennes.
Au cours de sa carrière politique, en 1975, elle fut nommée ministre de la protection de la famille et des affaires sociales et travailla avec ardeur à l’amélioration du statut des femmes dans son pays; c’était la première fois qu'une femme occupait un tel poste.
Ce travail consista notamment à promouvoir l’éducation des filles et des femmes, à lutter contre la pratique du gavage sur les jeunes femmes, à faire pression pour l’inclusion d’une disposition sur les droits maritaux et à plaider en faveur de la création d’un quota de représentation féminine au Parlement.
“[Aïssata] a réalisé toutes ses passions avec humilité, courage et détermination. Elle ne voulait déranger personne avec ce combat qu’elle menait sur tous les fronts à la fois.” Ball Halimata Dem, la nièce d’Aïssata
Ayant fondé l'Union nationale des femmes de Mauritanie (UNFM), elle avait cocréé et publié pour elles le magazine Marienou, dédié à l’émancipation des femmes mauritaniennes. Aïssata dirigea également plusieurs organisations sous-régionales et locales, notamment en tant que présidente de l'Association internationale des femmes francophones (AIFF) et, en écologiste résolue, fut présidente de l'Association pour la protection de l'environnement en Mauritanie (APEM).
En 2018, on lui décerna le Prix de la Femme africaine pionnière. Ce prix honore son engagement à faire progresser le statut de la femme en Mauritanie et reconnaît son grand leadership et son sens de l'innovation.
Aïssata est décédée le 10 août 2019.

Estamos monitoreando cuidadosamente este y otros riesgos, y publicaremos información integral sobre salud y seguridad cuando se abra la inscripción, para que puedas tomar una decisión informada. Además, el formato híbrido está diseñado para ofrecer una experiencia de participación significativa a quienes prefieran no viajar o no puedan hacerlo.

«Mientras estaba en la primera línea de la protesta, fui sometida a violencia sexual, a lesiones físicas y a otras formas de violencia. Pero no me detendré hasta que logremos pleno gobierno civil en Sudán. Debemos impedir la militarización del Estado. Nuestros cuerpos no deben seguir siendo tratados como campos de batalla»
dijo Amal,1 una manifestante de 23 años.2
Durante los últimos cuatro años, las mujeres lideraron la revolución en Sudán. Su liderazgo no fue solo callejero, sino que constituyó el poder que impulsó la resistencia constante en todos los niveles. Las mujeres y las jóvenes feministas se convirtieron en la conciencia alerta del movimiento de cambio y democratización sudanés. Desde la primera protesta del 13 de diciembre de 2018 contra el régimen anterior, en la ciudad de Aldmazein, en el área de conflicto del Nilo Azul, las jóvenes estudiantes fueron las voces que demandaron el fin de la dictadura de los militares y los Hermanos Musulmanes, que ya lleva treinta años en el poder.

El movimiento feminista, liderado por mujeres de entre 16 y 35 años, ha entablado una revolución dentro de la revolución en Sudán durante los últimos cuatro años de lucha ininterrumpida. Las potentes voces de las jóvenes que ocupan espacios en las calles, las redes sociales, la sociedad civil y las organizaciones políticas se elevaron lo suficiente como para reconfigurar la opinión pública y desafiar las normas sociales. Por primera vez en la historia de Sudán, las discusiones sobre violencia sexual y de género y sobre los tabúes de la violencia doméstica y los procesos de toma de decisiones dominados por los hombres se convirtieron en debates generalizados. Los equipos de fútbol de mujeres designaron voceras ante los comités de resistencia, y los sindicatos profesionales liderados por mujeres son parte de la expresión de la nueva ola del movimiento feminista de Sudán. El logro más importante es que las jóvenes se identifican como feministas en forma orgullosa y pública, en un país regido por el fundamentalismo islámico durante tres décadas. Los jóvenes varones que apoyan el activismo feminista -y se identifican como feministas- son otra señal de progreso notable.
Bajo el actual régimen del golpe militar, las jóvenes que lideran estas iniciativas y los grupos de mujeres que trabajan en el territorio no pueden mencionarse aquí debido a varios problemas de seguridad. Pero su resiliencia, su fuerza y su valentía serán incluidas en los libros de historia. Las audaces jóvenes que encabezan la resistencia en las calles y detrás de las pantallas, y que trabajan en diferentes profesiones y áreas de activismo están dando forma al futuro de Sudán. Las jóvenes feministas de Sudán están creando nuevos espacios para que las narrativas y los discursos feministas reestructuren la distribución del poder a nivel político, económico y social.
A pesar de la inmensa violencia, del resurgimiento del islamismo fundamentalista, de la militarización y de la reducción de los espacios cívicos, las activistas feministas de Sudán se mantienen arraigadas en su sororidad. Siguen siendo una gran inspiración para los movimientos feministas de todo el mundo.
Nazik Awad
1 «Amal» es un seudónimo utilizado para proteger a la joven activista citada.
2 Desde 2018, Sudán vive en una revolución constante. Una nueva ola opositora arrancó a partir del golpe militar del 25 de octubre de 2021.
ECONOMIAS DE CUIDADOSAGROECOLOGÍA Y SOBERANÍA ALIMENTARIACOOPERATIVISMO FEMINISTASINDICALISMO FEMINISTA
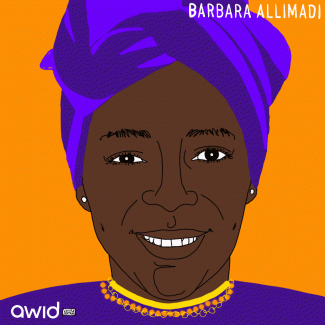
Barbara Allimadi was a political and human rights activist from Uganda. In 2012, she co-organized a protest against a televised police assault of Ingrid Turinawe, an opposition politician who had her breast squeezed by a police officer.
During the protest, Barbara, along with other fellow activists stripped to their bras in front of the Central Police Station in Kampala. This came to be known as the infamous ‘bra protest’ in Uganda.
“We settled on the bra protest. We thought it would be most appropriate for what had happened. It’s not like we were saying we don’t respect ourselves. We were disgusted by what had been done.” - Barbara Allimadi, 2013 (Daily Monitor)
With a Degree in Electronics and Communications Engineering from the London Metropolitan University, Barbara was a network engineer in the United Kingdom and an avid fan of reggae music. She returned to Uganda In 2007, when her mother passed away.
In 2019, she was appointed Coordinator for International and Diaspora Affairs at the Alliance for National Transformation (ANT), a political party launched that year by an opposition leader.
“We want security of life and property, not pain, injury and even death at the hands of security forces who are meant to protect us. Most importantly, we want a stable and enabling environment where we can realize our dreams and aspirations.” - Barbara Allimadi, ANT video
Barbara passed away on 27 April 2020.
“I was so proud of my sister for many things but in particular her fearless pursuit of peace, democracy, justice and equality in Uganda. At the height of her activism she led many marches on the streets of Kampala, to police stations, and Parliament.” - Doris Allimadi, Barbara’s sister
“It is with deep sadness that we have learnt of the untimely passing of Barbara Allimadi. She has been a valiant, relentless and courageous force for the liberation movement of Uganda. Our deepest condolences to her family. She will be sorely missed.” - Akina Mama wa Afrika (tweet on 28 April 2020)
“The passing on of Barbara is so sad for us and her entire family. She dedicated herself to fighting for justice, freedom and rights of others while serving in the civil society until she recently joined us at the party.” Maj Gen Mugisha Muntu, ANT national coordinator
“A beautiful, charming, funny, charismatic and inspirational sister. My children lost their aunty. Uganda lost a brave and courageous freedom fighter. Barbara once said, ‘As long as there is still breath in you, keep working towards your dreams.’” - Doris Allimadi, Barbara’s sister
L'AWID n'offre pas de tarif préférentiel pour les groupes, mais nous offrons des réductions d'inscription à nos membres. (Cliquez ici pour savoir comment devenir membre)
En la Comisión Africana y en el Sistema Interamericano, los actores antiderechos impulsan nociones esencialistas de cultura y género para impedir el avance de los derechos y socavar las responsabilidades. Como vemos, los actores anti-derechos están ejerciendo su influencia sobre los sistemas regionales de derechos humanos, así como en los espacios internacionales.


When thousands of feminists come together, we create a sweeping force of solidarity that has the power to change the world. The AWID Forum will be a moment for us to rest and heal together, connect across borders, and discover brave new strategic directions.
The date and location will be announced next year, as soon as we can. We’re excited and we know you’re excited too. Stay tuned!
Make sure to follow us on social media and subscribe to our mailing list to stay informed!
En 2023, las organizaciones feministas y por los derechos de las mujeres tenían un presupuesto anual promedio de USD 22.000. Detrás de ese promedio se esconde la disparidad y la desigualdad: mientras que algunos grupos acceden a recursos a gran escala, la gran mayoría apenas sobrevive con presupuestos muy ajustados.
Una mirada más detallada a los presupuestos reales revela gran diversidad y desigualdad de ingresos.
Consulta los datos sobre el tamaño de los presupuestos feministas
Yes! We are currently exploring innovating technologies to allow for meaningful connection and participation.
Vous voulez vous joindre au nombre croissant de personnes qui disent « ça suffit ! » face aux infiltrations des antidroits à l’ONU ?
