
Maha Abu-Dayyeh

Women human rights defenders (WHRDs) worldwide defend their lands, livelihoods and communities from extractive industries and corporate power. They stand against powerful economic and political interests driving land theft, displacement of communities, loss of livelihoods, and environmental degradation.
Extractivism is an economic and political model of development that commodifies nature and prioritizes profit over human rights and the environment. Rooted in colonial history, it reinforces social and economic inequalities locally and globally. Often, Black, rural and Indigenous women are the most affected by extractivism, and are largely excluded from decision-making. Defying these patriarchal and neo-colonial forces, women rise in defense of rights, lands, people and nature.
WHRDs confronting extractive industries experience a range of risks, threats and violations, including criminalization, stigmatization, violence and intimidation. Their stories reveal a strong aspect of gendered and sexualized violence. Perpetrators include state and local authorities, corporations, police, military, paramilitary and private security forces, and at times their own communities.
AWID and the Women Human Rights Defenders International Coalition (WHRD-IC) are pleased to announce “Women Human Rights Defenders Confronting Extractivism and Corporate Power”; a cross-regional research project documenting the lived experiences of WHRDs from Asia, Africa and Latin America.
"Women Human Rights Defenders confronting extractive industries: an overview of critical risks and Human Rights obligations" is a policy report with a gender perspective. It analyses forms of violations and types of perpetrators, quotes relevant human rights obligations and includes policy recommendations to states, corporations, civil society and donors.
"Weaving resistance through action: Strategies of Women Human Rights Defenders confronting extractive industries" is a practical guide outlining creative and deliberate forms of action, successful tactics and inspiring stories of resistance.
The video “Defending people and planet: Women confronting extractive industries” puts courageous WHRDs from Africa, Asia, and Latin America in the spotlight. They share their struggles for land and life, and speak to the risks and challenges they face in their activism.
Challenging corporate power: Struggles for women’s rights, economic and gender justice is a research paper outlining the impacts of corporate power and offering insights into strategies of resistance.
AWID acknowledges with gratitude the invaluable input of every Woman Human Rights Defender who participated in this project. This project was made possible thanks to your willingness to generously and openly share your experiences and learnings. Your courage, creativity and resilience is an inspiration for us all. Thank you!
Le thème du 14e Forum international de l'AWID est «Réalités féministes : notre pouvoir en action».
Ce Forum célébrera et amplifiera les propositions audacieuses autour de nous, à tous les stades de déveoppement !

طبعاً! هذه الأسئلة اختيارية. نقدّر جداً حقكم بالسرية. الرجاء تعبئة الاستطلاع دون علاقة بقراركم/ن بمشاركة اسم المجموعة، المنظمة أو الحركة أو تفاصيل التواصل معكم/ن.
Lo personal es político, y la apasionada y valiente Nadyn Jouny personificó este mantra feminista. Nadyn experimentó de primera mano el dolor de la violencia estructural de los sistemas legales que despojan a las mujeres de sus derechos.
Cuando Nadyn decidió solicitar el divorcio, los tribunales religiosos chiítas, bajo las Leyes de Estatuto Personal Libanesas, le negaron la custodia de su joven hijo Karam. Nadyn, como tantas otras mujeres del Líbano y de otros países, se vio atrapada entre el dolor imposible de dejar una relación no deseada y abusiva y de perder a la vez los derechos sobre su hijo. Sin embargo, Nadyn se defendió, y lo habría de hacerlo hasta el último día.
Nadyn utilizó su habilidad con los medios de comunicación para convertirse en una voz franca a favor de las mujeres que luchan contra la discriminación en la legislación familiar, en el Líbano y a nivel internacional. Nadyn cofundó el grupo autofinanciado "Protecting Lebanese Women" [Protegiendo a las Mujeres Libanesas] (PLW, por sus siglas en inglés) y se unió a muchas otras madres libanesas que se enfrentaban a problemas similares de custodia. Juntas, trabajaron para crear conciencia sobre las injusticias extremas a las que se enfrentaban, a nivel nacional, protestaron ante los tribunales religiosos por sus derechos y, a nivel internacional, llamaron la atención de los medios de comunicación.
Nadyn también trabajó con ABAAD - Resource Center for Gender Equality [Centro de Recursos para la Igualdad de Género], otra organización por los derechos de las mujeres en el Líbano, para realizar campañas en favor de los derechos de las mujeres, la igualdad en la legislación familiar y relativa a las custodias y contra los matrimonios forzados y precoces.
Para muchxs de sus colegas, Nadyn llegó a "simbolizar la lucha de una madre libanesa contra la supresión y la misoginia de todo tipo" (en inglés), al utilizar "su experiencia personal y trayectoria individual de empoderamiento, dio a otras mujeres esperanza para que ellas también pudieran ser un catalizador para el cambio positivo" - ABAAD - Centro de Recursos para la Igualdad entre los Géneros, Líbano.
El 6 de octubre de 2019, Nadyn murió trágicamente en un accidente de automóvil cuando se dirigía a protestar por los injustos aumentos de impuestos en un país que ya se enfrentaba a una espiral de crisis financiera. Nadyn Jouny tenía solo 29 años en el momento de su muerte.
Sesiones adicionales para redactar el Documento Final de Adís Abeba
Para saber más sobre este proceso, puedes consultar la CSO Hitchhiker’s Guide (en inglés).


Да, пожалуйста! Мы просим распространить ссылку на опрос среди своих коллег по сети. Чем больше различных точек зрения мы соберем, тем более полным будет наше понимание финансового положения феминистских организаций.
Doris Valenzuela Angulo était une activiste sociale, leader et défenseure des droits humains afrodescendante de Buenaventura, en Colombie. Elle faisait partie du réseau national Comunidades Construyendo Paz en Colombia (CONPAZ, Communautés construisant la paix en Colombie) composé d’organisations présentes dans les communautés affectées par le conflit armé œuvrant en faveur de la non-violence et la justice socio-environnementale.
Doris s’opposait à la violence paramilitaire continue, aux pressions incessantes des mégaprojets cherchant à déplacer sa communauté, et à la complicité de l’État. Confrontée à l’un des contextes les plus difficiles de son pays, elle joua un rôle de premier plan dans l’initiative de résistance non-violente sans précédent Espacio Humanitario Puente Nayero, un lieu urbain conçu pour assurer la cohésion communautaire, la sécurité, la créativité et l’action collective.
Ce combat non-violent unique en son genre des familles de l’Espacio Humanitario Puente Nayero attira l’attention et le soutien des agences tant locales qu’internationales. En septembre 2014, la Commission interaméricaine des droits de l’Homme accorda des mesures de protection préventives à la communauté, ordonnant au gouvernement colombien d’adopter des mesures nécessaires en vue de protéger la vie et l’intégrité physique des habitant·e·s. Les menaces et la violence des paramilitaires se poursuivirent néanmoins. Malgré l’assassinat de son fils Cristian Dainer Aragón Valenzuela en juillet 2015,Doris continua à mettre toute son énergie à éviter le recrutement forcé des enfants et des jeunes par les néo-militaires. Elle devint alors également une cible, recevant constamment des menaces pour son activisme et le travail qu’elle accomplissait.
Les incessantes agressions et menaces de mort dont elle était l’objet forcèrent Doris à quitter la Colombie. Elle vécut en Espagne de février 2017 à février 2018, dans le cadre du programme de protection temporaire d’Amnesty International pour les défenseur·e·s des droits humains en danger.
Doris a été assassinée en avril 2018 à Murcie, en Espagne, par son ex-compagnon. Elle n’avait que 39 ans.
« Doris, cette année passée avec toi nous a montré combien une personne peut avoir la capacité de transformer et créer de l’espoir en dépit des événements profondément négatifs et dévastateurs qui jalonnent sa vie... Nous poursuivons notre engagement à défendre tous les droits humains. Ton courage et ta lumière nous guideront toujours. » - Montserrat Román, Amnesty International, Groupe de La Palma, Espagne
« ... Tu le savais. Tu l’as toujours su. Et malgré tout cela, tu as résisté sans faillir à tant d’injustice, de misère, de persécution. Tu t’es élevée, fière et acharnée, contre ceux qui continuaient à vouloir que tu abandonnes tout espoir, que tu t’abaisses, que tu te rendes. Debout, tu as réclamé haut et fort ta liberté et la nôtre, qui était la tienne. Rien ni personne n’est parvenu à paralyser tes efforts pour changer le monde et le rendre plus généreux et plus vivable. Tu vis parmi nous, aujourd’hui plus vivante que jamais malgré la mort. Tu vis encore par tes actes, par ton courage, par ta grandeur lorsque tu pleurais pour cette terre promise que tu invoquais à chacun de tes cris, pour tous ces déserts que tu as habités. Toi. Toujours en vie. Doris Valenzuela Angulo.
Ce ne sont que des mots. Je sais. Je le sais, moi aussi. Mais les mots nous unissent, nous protègent, nous donnent la force et le soutien nécessaires pour continuer à aller vers la lumière que tu défendais tant... »
‘A geopolitical Analysis of Financing for Development’ by Regions Refocus 2015 and Third World Network (TWN) with DAWN.
The Zero Draft Language Map, by Regions Refocus
‘Addis Ababa financing conference: Will the means undermine the goals?‘ by RightingFinance
por Rode Wanimbo
«Señor, somos indignas. Somos las que pecaron, porque Eva comió el fruto en el Edén. Solo somos mujeres que cultivan batatas, cuidan cerdos y dan a luz niñxs. Creemos que tú moriste en la cruz para liberarnos. Gracias, en el nombre de Jesús, amén». (...)
< arte: «Offerings for Black Life» [Ofrendas para las vidas negras], Sokari Ekine

I believe empowered women empower women and that is why I’ve had an incredible time being an AWID member. My knowledge and understanding of Feminism and intersectionality has been broadened by the exposure I received being part of the AWID Community Street Team. I hope more women join and share topics and ideas that will help other women.
- Loyiso Lindani, South Africa.
Nos entusiasma compartir nuestro nuevo Plan Estratégico (2023-2027) con el mundo. Próximamente, AWID anunciará a nuestra comunidad y membresía al respecto.
La Asociación para los Derechos de las Mujeres y el Desarrollo es una organización feminista mundial, de membresía, que se dedica a brindar apoyo a los movimientos.
Por más de 35 años hemos formado parte de un increíble ecosistema de movimientos feministas que trabajan para alcanzar la justicia de género y los derechos humanos de las mujeres de todo el mundo.

AWID imagina un mundo donde las realidades feministas florezcan, donde los recursos y el poder sean compartidos de maneras que permitan a todxs, y a las generaciones futuras, prosperar y concretar plenamente su potencial con dignidad, amor y respeto, y donde la Tierra nutra la vida en toda su diversidad.
Nuestra misión es apoyar a los movimientos feministas, de derechos de las mujeres y por la justicia de género para que progresen y para que sean una fuerza impulsora de retos a los sistemas de opresión y para la creación conjunta de realidades feministas.
Desarrollamos nuestro trabajo a través de estas tácticas:
Hacemos uso colaborativo de nuestro acceso, poder, recursos y relaciones para influir estratégicamente sobre las políticas y las prácticas. Nos proponemos impulsar agendas feministas a través de nuestro trabajo con quienes tienen poder de decisión política, con financiadoras y con activistas en los espacios regionales y mundiales. Para reforzar nuestro poder e influencia colectivos, también procuramos influir sobre los movimientos feministas y de derechos de las mujeres para que pongan en lugar central a los movimientos históricamente oprimidos.
Utilizamos nuestro poder de convocatoria para facilitar el diálogo y pensar estrategias sobre temas clave. Conectamos a nuestra membresía y aliadxs entre sí, para que compartan e intercambien recursos, ideas y acciones sobre temas relevantes. Organizamos y facilitamos espacios en los que participan y se fortalecen diversos movimientos, espacios para imaginar y concebir nuevos futuros, para desarrollar tácticas de influencia efectivas y para crear juntxs agendas y procesos transformadores.
Trabajamos para movilizar a nuestra membresía y a los movimientos que apoyamos para fortalecer la acción colectiva en solidaridad con causas feministas y con lxs defensorxs que están en peligro. Construimos colaboraciones de largo plazo, nos comprometemos en la escucha activa y la solidaridad continua. Trabajamos con defensorxs para construir conocimiento, redes de apoyo y solidaridad para la protección y el bienestar.
Reconocemos el valor único y estratégico de las iniciativas culturales y creativas en la lucha contra la opresión y la injusticia. Trabajamos con artistas que le dan un lugar central a las voces feministas y a las narrativas de la comunidades históricamente oprimidas. En esta táctica emergente, vemos al arte y la expresión creativa como algo que nos ayuda a concebir un mundo donde las realidades feministas siguen floreciendo y sigan siendo celebradas.

Nuestras iniciativas trabajan en las intersecciones de escenarios de cambio que buscamos abordar, de los movimientos que priorizamos y de las tácticas que usamos:
Monitoreamos, documentamos y hacemos visible cómo están operando y aglutinándose lxs actorxs anti-derechos en los espacios multilaterales y apoyamos a los movimientos feministas, de derechos de las mujeres y por la justicia de género y sus aliadxs para contrarrestar esa influencia e impacto.
Desde perspectivas como el extractivismo, la justicia impositiva y la rendición de cuentas corporativa, construimos conocimiento sobre el poder corporativo y su influencia; abogamos por que las empresas asuman sus responsabilidad así como por la distribución equitativa de la riqueza, y amplificamos las propuestas feministas para lograr economías justas.
Desarrollamos análisis accesibles y orientados a la acción acerca del estado del financiamiento para los movimientos feministas. Nos proponemos influir sobre las políticas y prácticas de las financiadoras, incrementar y sostener el financiamiento para el cambio social feminista, y apoyar las necesidades y estrategias de los movimientos.
Además del impacto que pretendemos tener en el mundo, AWID está expresamente comprometida con el fortalecimiento de nuestro propio aprendizaje y resiliencia organizacionales, para poder fortalecer mejor a los movimientos feministas del mundo.
¡Muchas Gracias!
Sin el generoso aporte y apoyo de nuestros donantes, nuestro trabajo no sería posible.
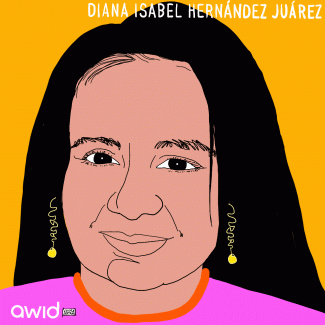
Diana Isabel Hernández Juárez was a Guatemalan teacher, human rights defender and environmental and community activist. She was the coordinator of the environmental program at Our Lady of Guadalupe Parish on the South coast of the country.
Diana dedicated her life to co-creating environmental awareness, working especially closely with local communities to address environmental issues and protect natural resources. She initiated projects such as forest nurseries, municipal farms, family gardens and clean-up campaigns. She was active in reforestation programmes, trying to recover native species and address water shortages, in more than 32 rural communities.
On 7 September 2019, Diana was shot and killed by two unknown gunmen while she was participating in a procession in her hometown. Diana was only 35 years old at the time of her death.
作為對AWID論壇各方面可訪問性承諾的一部分,我們接受那些無法提交書面申請的個人/組織/團體提交自己的音頻或視頻等。
如果您選擇以音頻/視頻格式提交提案,請按照相同的順序回答活動申請表格中詳細的問題。
若您要提交音頻/視頻文件,請與我們聯繫,選擇“論壇活動徵集”作為電子郵件的主題。
Nous sommes ravi.es d'annoncer le lancement du nouveau podcast de l'AWID, NOTRE FLAMME FÉMINISTE. Notre série narrative dévoile plus de 40 ans de mouvements féministes et réinvente une voie à suivre.
Dans notre saison pilote, vous entendrez cinq histoires captivantes qui font partie d'une constellation d'activisme féministe aujourd'hui. Animé par Gopika Bashi, notre directrice adjointe des programmes à l'AWID, chaque épisode explore des réalités féministes uniques mais interconnectées qui améliorent la justice de genre et les droits humains.
Produit par notre partenaire de podcast Webby Hueman Group Media, vous pouvez vous abonner à NOTRE FLAMME FÉMINISTE et écouter notre premier épisode ici.
Retrouvez-nous sur Apple Podcasts, Spotify ou partout où vous obtenez vos podcasts. Partagez avec votre réseau ! Aidez-nous à diffuser des histoires qui allument notre feu féministe et nous poussent à l'action.
par Marta Plaza Fernández
Le pouvoir de tisser des réseaux où nous nous soutenons les unes les autres: telle est la réalité féministe dont je veux vous faire part. (...)
illustration : « Guérir ensemble », par Upasana Agarwal >