
Yusdiana

WHRDs are self-identified women and lesbian, bisexual, transgender, queer and intersex (LBTQI) people and others who defend rights and are subject to gender-specific risks and threats due to their human rights work and/or as a direct consequence of their gender identity or sexual orientation.
WHRDs are subject to systematic violence and discrimination due to their identities and unyielding struggles for rights, equality and justice.
The WHRD Program collaborates with international and regional partners as well as the AWID membership to raise awareness about these risks and threats, advocate for feminist and holistic measures of protection and safety, and actively promote a culture of self-care and collective well being in our movements.
WHRDs are exposed to the same types of risks that all other defenders who defend human rights, communities, and the environment face. However, they are also exposed to gender-based violence and gender-specific risks because they challenge existing gender norms within their communities and societies.
We work collaboratively with international and regional networks and our membership
We aim to contribute to a safer world for WHRDs, their families and communities. We believe that action for rights and justice should not put WHRDs at risk; it should be appreciated and celebrated.
Promoting collaboration and coordination among human rights and women’s rights organizations at the international level to strengthen responses concerning safety and wellbeing of WHRDs.
Supporting regional networks of WHRDs and their organizations, such as the Mesoamerican Initiative for WHRDs and the WHRD Middle East and North Africa Coalition, in promoting and strengthening collective action for protection - emphasizing the establishment of solidarity and protection networks, the promotion of self-care, and advocacy and mobilization for the safety of WHRDs;
Increasing the visibility and recognition of WHRDs and their struggles, as well as the risks that they encounter by documenting the attacks that they face, and researching, producing, and disseminating information on their struggles, strategies, and challenges:
Mobilizing urgent responses of international solidarity for WHRDs at risk through our international and regional networks, and our active membership.


Préparée par Jess X. Snow
avec l’aide de Kamee Abrahamian et Zoraida Ingles
Révisée par Kamee Abrahamian
Dans toute l’Asie et le Pacifique, et dans sa diaspora tout entière, des femmes et des trans farouches se battent pour un avenir où iels pourraient être libres. Alors que l’élévation du niveau des mers menace les îles du Pacifique et les côtes de l’Asie continentale, la lutte pour protéger la Terre et les océans s’intensifie dans le monde entier. La mémoire géologique de notre planète enregistre toutes les expériences qu’elle a vécues : la montée des colonisations, de l’industrialisation et de la destruction de l’environnement est liée à la montée de l’État-nation patriarcal binaire. Le pouvoir au sein de la Terre de se réincarner et d’éclore face à la violence doit alors être mis en lien avec les femmes, la maternité, l’indigénéité et toutes les forces expansives, sacrées et queer. Les Réalités féministes unissent la lutte pour la protection des droits des femmes, des trans et des personnes LGBTQ+ avec celle pour la protection de la Terre, et ce n’est pas une coïncidence. Des mères et filles protégeant le Mauna Kea au Royaume de Hawai’i aux relations complexes entre mères et enfants chez les réfugié·e·s du Vietnam, en passant par les réveils sexuels de personnes queer dans l’Inde conservatrice, la réclamation de la construction de maisons en Mongolie intérieure et la lutte pour la libération des personnes LGBTQ aux Philippines, cet ensemble de films est une constellation des manières selon lesquelles les femmes, personnes queer et trans en Asie-Pacifique défendent de nos jours les multiples voies vers notre libération collective, au-delà des océans et des frontières.
Tous ces films témoignent du sens fort accordé aux lieux : des activistes autochtones protègent leurs terres sacrées, des jeunes déconstruisent les récits coloniaux sur leurs terres et découvrent des vérités cachées, les liens complexes de maternité et de soins sont examinés, et des personnages se tournent vers leur propre corps et leur sexualité comme autant de sanctuaires, lorsque la famille et la ville qui les entourent menacent leur sécurité.
De Jess X. Snow
« Un film envoûtant avec des plans époustouflants qui invoquent la résistance écologique féministe et comment elle prend directement source dans l'histoire culturelle et la terre… »
- Jessica Horn, stratège féministe panafricain·e, écrivain·e et cocréateur·rice de The temple of her skin (Le temple de sa peau)
Dans le documentaire expérimental Afterearth, quatre femmes se battent pour protéger les volcans, les océans, la terre et l’air pour les générations futures. En s’appuyant sur de la musique, de la poésie et le témoignage poignant qui rend honneur aux lieux qu’atteint l’océan Pacifique – Hawai’i, les Philippines, la Chine et l’Amérique du Nord, Afterearth est une méditation poétique sur la relation intergénérationnelle et féministe de quatre femmes avec les terres et les plantes dont elles sont issues.
De Jalena Keane Lee
Dans Standing Above the Clouds, des mères et filles activistes indigènes de Hawai’i se tiennent côte à côte pour protéger leur montagne sacrée, Mauna Kea, contre sa transformation en un site de construction des plus grands télescopes au monde. En tant que protectrices de Mauna Kea, ce film souligne l’interconnexion entre Aloha ʻĀina (l’amour de la terre) et l’amour pour ses aîné·e·s et les générations à venir.
De Quyên Nguyen-Le
Dans ce court-métrage narratif expérimental, Nước (Eau/Terre natale) un·e ado genderqueer vietnamo-américain·e questionne les récits dominants sur la guerre du Vietnam à Los Angeles, Californie. Par le jeu de séquences oniriques fortes et d’intrusions de la réalité, ce film suit le parcours qui lui permet de recomposer et de comprendre l’expérience de sa mère, réfugiée de la guerre du Vietnam.
De Kimi Lee
Dans Kama’āina, une jeune queer de seize ans doit se débrouiller pour vivre dans les rues de Oahu, jusqu’à ce qu’elle finisse par pouvoir se réfugier, sur les conseils d’une tata, à Pu’uhonua o Wai’anae, le plus gros camp organisé de sans-abris de Hawai’i.
By Karishma Dev Dube
Dans Devi (« déesse » en hindi), Tara, une jeune lesbienne « dans le placard », s’oppose à la fois à sa famille et à la tradition pour vivre son attirance pour la servante de la maison. Située à New Delhi, Devi est une histoire de révélation tout autant qu’un commentaire sur les lignes sociales et de classe qui divisent les femmes de l’Inde contemporaine.
De Yuan Yuan
Dans Heading South, Chasuna, une fillette de 8 ans élevée par sa mère sur le Plateau de la Mongolie intérieure, rend visite à son père abusif à la grande ville. Pendant qu’elle est chez son père, on lui présente une nouvelle venue dans la famille. Elle doit alors reconnaître et accepter que sa véritable maison est inséparable de sa mère et de la terre.
De Johnny Symons & S. Leo Chiang
Dans le long métrage Outrun, nous suivons le parcours de la première femme transgenre au Congrès des Philippines. Face à l’oppression d’une nation majoritairement catholique, son parcours victorieux devient un cri de victoire pour les droits des personnes LGBTQ+ du monde entier.
Alliant le documentaire, le récit et des formes expérimentales, ces films illustrent que l’attention de la communauté, l’amour de soi et une écoute profondément transformatrice entre celleux que nous aimons sont une entrée dans les Réalités féministes auxquelles nous donnons vie aujourd’hui. De toute l’Asie Pacifique et sa diaspora, ces histoires nous montrent que, face à la violence, la tendresse est la plus féroce des résistances.
Regardez notre conversation avec les cinéastes
Facebook: @AWIDWomensRights
Instagram: @awidwomensrights
Twitter ENG: @awid
Twitter ES: @awid_es
Twitter FR: @awid_fr
LinkedIn: Association for Women's Rights in Development (AWID)

 |
Derechos humanos y etnico-territoriales Asegurar la defensa de los derechos humanos y los derechos de la Naturaleza a través de la construcción de alianzas con actores y organizaciones locales, nacionales, regionales y globales. |
 |
Desarrollo Sostenible Garantizar que todas las actividades económicas, culturales y ambientales contribuyan al desarrollo sostenible, la seguridad alimentaria y la generación de ingresos, respetando la libre determinación y el autogobierno de las comunidades afrodescendientes. |
 |
Educación y formación Capacitar y empoderar mujeres para que defiendan sus derechos en diferentes espacios políticos, sociales y económicos. ¡Para obtener más información, puedes ver más aquí! |

Anti-rights discourses continue to evolve. As well as using arguments related to religion, culture, and tradition, anti-rights actors co-opt the language of social justice and human rights to conceal their true agendas and gain legitimacy.

Three decades ago, a US television evangelist and Republican candidate famously said that feminism is an “anti-family political movement that encourages women to leave their husbands, kill their children, practice witchcraft, destroy capitalism and become lesbians.” Today, this conspirative notion gains unprecedented grasp and legitimacy in the form of “gender ideology” discourse, a catch-all bogey-man created by anti-rights actors for them to oppose.
Across a range of discourses employed by anti-rights actors - including notions of “cultural imperialism” and “ideological colonization”, appeals to “conscientious objection” and the idea of a “pre-natal genocide” - a key theme is co-optation. Anti-rights actors take legitimate issues, or select parts of them, and twist them in service of their oppressive agenda.

En vous promenant dans le quartier du Raval à Barcelone, vous croiserez peut-être Metzineres, une coopérative féministe par et pour les femmes et personnes trans et non-binaires qui consomment de la drogue.
Imaginez un endroit sans stigmatisation, où les femmes et personnes trans et non-binaires peuvent consommer des drogues en toute sécurité. Un lieu qui offre sécurité, soutien et accompagnement aux femmes et personnes trans et non-binaires dont les droits sont systématiquement bafoués par la guerre contre la drogue et qui subissent violence, stigmatisation et répression en conséquence.
Juste à l'extérieur de l'entrée, les passant·es et les visiteur·euses sont accueilli·e·s par un immense tableau noir où figurent des conseils, des astuces, des souhaits et des dessins de personnes qui consomment de la drogue. Il existe également un calendrier qui présente une série d'activités auto-organisées par la communauté Metzineres. Qu'il s'agisse d'ateliers coiffure et cosmétique, des émissions radio, des pièces de théâtre, de repas communs offerts à la communauté ou des cours d'autodéfense, il y a toujours quelque chose à faire!
La coopérative offre des sites de consommation sûrs ainsi que des services qui couvrent les besoins de base des gens. Il y a des lits, des casiers, des douches, des toilettes, des machines à laver et une petite terrasse extérieure où les gens peuvent se détendre ou jardiner.
Metzineres opère dans un cadre de réduction des méfaits, qui tente de réduire les conséquences négatives de la consommation de drogue. Mais la réduction des méfaits est bien plus qu'un ensemble de pratiques: c'est une politique ancrée dans la justice sociale, la dignité et les droits des personnes qui consomment des drogues.

![]()
La encuesta está disponible en árabe, español, francés, inglés, portugués y ruso.
 |
Hind and Hind were the first documented queer couple in Arab history. In today’s world, they are a queer artist from Lebanon. |

When I was 6, I learned that my grandfather owned a movie theater. My mother recounted to me how it had opened in the early 1960s, when she was also about 6 years old. She remembered that they screened The Sound of Music on the first night.
I would pass by the theater every weekend and watch my grandfather play backgammon with his friends. I didn’t know he was living in the theater, in a room right under the projection booth. I later learned that he moved there after he and my grandmother separated and after the theater closed, in the 1990s, shortly after the Lebanese civil war had ended.

For years and until he passed away, I would mostly see my grandfather play backgammon in the unmaintained reception area of the movie theater. Those repeated scenes are all I remember of him. I never got to properly know him; we never talked about cinema, even though he spent all his time in a run-down movie theater. I never asked him what it was like to live in a place like this. He died when I was 12, on Christmas Eve, from a fall down the spiraling steps that led to the projection booth. It is almost poetic that he passed away in movement, in a house where moving images are perpetually suspended in time.

In the spring of 2020, my cousin called me to say he had cleaned up my grandfather’s movie theater and asked me to meet him there. The two of us had always dreamed of renovating it. I got there before he did. In the reception area, the film poster frames were still there but the posters were gone. I knew there must have been some ticket stubs left somewhere; I found them stacked away in a small rusty tin box, on a shelf in the ticketing booth, and I pocketed some.
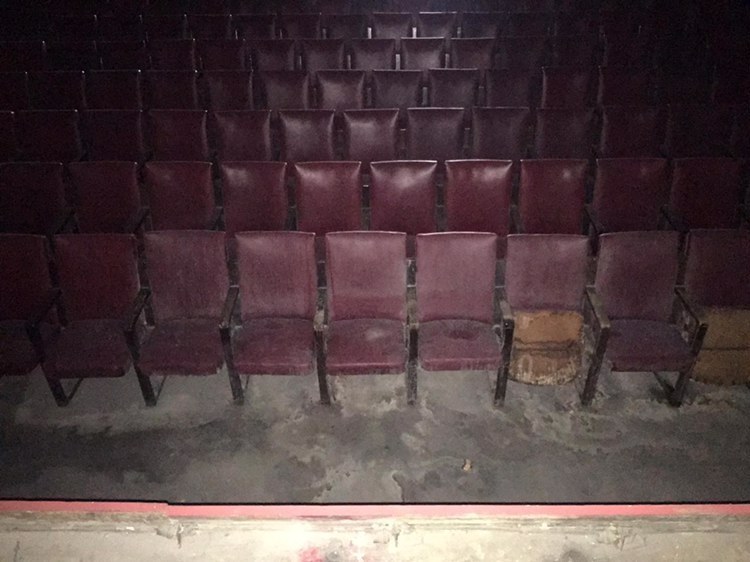
I began to walk around. On the main stage, the projection screen was quite dirty and a little torn on the side. I glided my index finger on the screen to remove a patch of dust and noticed that the screen was still white underneath. The fabric seemed to be in good shape too. I looked up to see that my grandmother’s curtains were still in place. They were made of white satin with a little embroidered emblem over the bridge of the curtain, representing the theater. There was a main seating area and a gallery. The chairs seemed to be very worn out.
I noticed the projector peeking out of a small window at the very end of the balcony seating area. I led myself up the spiraling steps of the projection booth.
The room was dark, but a source of light coming from the dusty windows revealed a stack of film reels tossed in a corner. Lifeless celluloid strips were tangled up against the foot of the film projector. The dusty reels were all Western, Bollywood, and Science-Fiction genre films with bad titles like The Meteor that Destroyed Earth, or something of the sort. My attention was caught by the dusty film strips – mostly snippets cut out from reels. One by one, the short strips depicted different kissing scenes, what seemed like a suggestive dance, a nondescript scene of a gathering, a close-up of a woman lying down with her mouth open, opening credits to a Bollywood film, and a “Now Showing” tag that went on for several frames.
The Bollywood film credits reminded me of my mother. She used to tell me how they would hand out tissues to audience members on their way out of screenings. I kept the kissing scene and suggestive dance strips; I assumed they had been cut out for censorship reasons. The close-up of the woman reminded me of an excerpt from Béla Balázs’ Visible Man, or The Culture of Film, The Spirit of Film, and Theory of the Film. He said that close-ups in film provided a
silent soliloquy, in which a face can speak with the subtlest shades of meaning without appearing unnatural and arousing the distance of the spectators. In this silent monologue, the solitary human soul can find a tongue more candid and uninhibited than any spoken soliloquy, for it speaks instinctively, subconsciously.

Balázs was mostly describing the close-ups of Joan in the silent film La Passion de Jeanne d’Arc. He pointed out how, “...in the silent (movie), facial expression, isolated from its surroundings, seemed to penetrate to a strange new dimension of the soul.”
I examined the film strip further. The woman looked dead, her face almost mask-like. She reminded me of Ophelia by the painter John Everett Millais. In her book On Photography, Susan Sontag says a photograph is “a trace, something directly stenciled off the real, like a footprint or a death mask.” These death masks are like a presence that reminds of an absence.
I remembered encountering a discourse between death and photography in Roberto Rossellini’s forgotten film The Machine that Kills Bad People. In this film, a cameraman goes around taking photographs of people, who would in turn freeze, and are later suspended in time. French film critic André Bazin used to say that photography snatches bodies away from the flow of death and stores them by embalming them. He described this photographic mummification as “the preservation of life by a representation of life.”
This projection booth, its whole layout, all the things that looked like they were moved, the celluloid strips on the ground, everything my grandfather left a mark on – I felt very protective of.
Underneath the strips was an undone dusty film reel. It seemed like someone had been watching the reel manually. At that moment, my cousin made his way up the spiraling steps to find me examining it. He rubbed his fingers along his chin and, in a very-matter-of-fact way, said, “You found the porn.”
I looked at the film strip in my hand and realized it was not a death scene. The strip was cut out of the porn reel. The woman was moaning in ecstasy. Close-ups are meant to convey feelings of intensity, of climax, but I had never really used Balázs’ theories to describe a porn scene. He wrote how “the dramatic climax between two people will always be shown as dialogue of facial expressions in close-up.” I pocketed the film strip and I named the woman Ishtar. She has lived in my wallet ever since. It seemed strange to compare the close depiction of Joan’s fears and courage with Ishtar’s facial expression in ecstasy.
According to my cousin, my grandfather’s brother would wait until my grandfather left the theater and, instead of closing, invite his friends for some after-hour private screenings. I didn’t think much of it. It was a common practice, especially during and after the Lebanese civil war. After the war, television sets were almost in every Lebanese household. I even remember having one in my bedroom in the late 1990s, when I was around 6 years old. I was told that buying porn films on VHS was popular at the time. Mohammed Soueid, a Lebanese writer and filmmaker, once told me that movie theaters used to screen art films and pornography from the mid-1980s to the mid-1990s, so that they could survive. I also heard that projectionists would cut up porn reels to make different montages, so that they could screen something different every night. Eventually, people stayed within the comforts of their homes to watch VHS tapes on their televisions, and movie theaters began to run out of business.

My cousin went back downstairs to go through an archive of paperwork in the office space. I stayed in the booth and began to slip the film strip between my index and middle finger, sliding it up with my thumbs and slowly running the frames through my hands. I lifted the strip against the dusty window and squinted to make sense of the monochrome vignettes. In this series of frames was an extreme close-up of a dick shoved into a vagina. It went on for several frames until I came across a knot in the film, and I imagined the rest.


Hank is showcasing his hard-on in front of Veronika who is lying in bed across a Louis XIV secrétaire knockoff. She gets up slowly and slides the thin strap of her see-through négligé off her left shoulder. Hank unties her veiled robe, turns her around, slaps her ass, and pushes her down against the secrétaire. He thrusts his dick inside her pussy repeatedly as the back of the furniture bangs against the wallpaper-adorned wall.

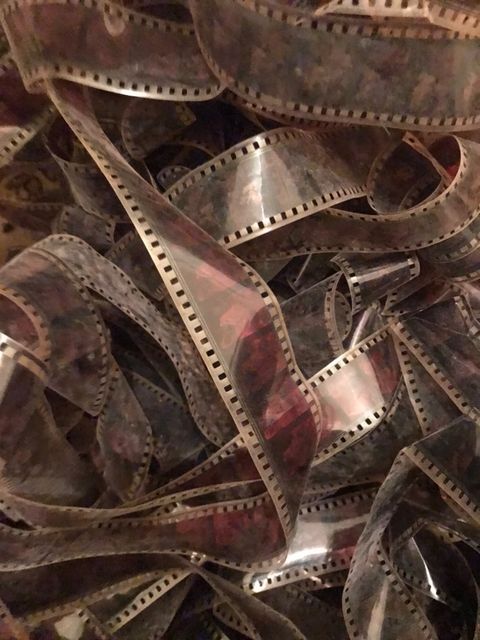
I was always attentive to the interior décor, ever since I was told by my Women in Porn Studies professor that the largest porn archives in North America are interestingly used to examine the middle-class furniture of that epoch. So, while Veronika is bending over and being taken from behind by Hank, a university research assistant could very well be trying to guess the design of the gold motif on the secrétaire, or study the rococo relief on a wooden chair in some corner.
For a moment, the booth became a space for female sexual imagination, disrupting a space otherwise promised for the freedom of male sexuality. I was sure that only men were able to access movie theaters that screened porn films. The film reel was too entangled to undo in a projection booth where dust had accumulated for over a decade, so I stuffed it into my duffle bag and walked out of the theater.
I am not sure what came over me, but I felt compelled to keep it. I wanted to feel the thrill of safeguarding something mysterious, something unorthodox. In my mind, I was sure people knew I was hiding something as I walked down the street. A feeling of guilt intertwined with pleasure came over me. It felt kinky.

I got into the house, preoccupied with the thought of having a porn reel in my duffle bag and the stream of thoughts that had unfolded on my walk home. I immediately went to my bedroom. In some distant part of my mind, I remembered that I shared a wall with Layla’s room next door. She was probably not home, but the possibility of being heard excited me. I closed my bedroom door and I took the film strip of Ishtar out.
I imagined her dressed in a light green veiled dress, dancing seductively in front of me, swinging her hips sideways and smiling with her eyes. I got onto my bed. I slipped my fingers into my panties. I lifted my hips. I trailed my hand down my thighs to part them, and slid two fingers in. I tensed up as I palpated my various creases. I moaned before I could stop myself. I panted and swayed. The rays of sun coming through my window planted reluctant kisses onto my skin. I held my breath in and my limbs quivered. I swallowed my breath and laid flat on the mattress.

When I was an undergraduate student, I had taken an introductory film class and Professor Erika Balsom had scheduled a screening of Bette Gordon’s Variety. I was excited to watch producer Christine Vachon’s first film before she moved onto producing films that are now part of the New Queer Cinema movement. Variety was described as a feminist film about Christine, a woman who begins to work as a ticketing clerk in a porn movie theater in New York city called The Variety Theater. Christine overhears the films at the theater but never goes in. Eventually, she becomes interested in a regular customer, whom she watches closely. She follows him to an adult shop where she stands aside and flips through adult magazines for the first time.
Christine’s voyeurism was displayed in different ways throughout the film. The script was also ridden with excess, and erotic monologues that would be considered obscene or vulgar.
In a scene set in an arcade, she reads erotica to her boyfriend. The camera goes back and forth between a close-up of her boyfriend Mark’s butt as he was playing pinball, swinging his hips back and forth against the arcade machine, and a close-up of Christine’s face as she recited her monologue.


“Sky was hitchhiking and he got a ride from a woman in a pick-up truck. It was late at night and he needed a place to stay, so she offered him her place.
She showed him to his room and offered him a drink. They drank and talked and decided to turn in. He couldn’t sleep, so he put on his pants and walked down the hall to the living room. He was a stop short of being seen, but he could see. The woman was naked and spread on the coffee table with only her legs dangling over. Her whole body was excitingly white as if it’d never seen the sun. Her nipples were bright pink, fire-like, almost neon. Her lips were open. Her long auburn hair licking the floor, arms stretched, fingers tickling the air. Her oiled body was round with no points, no edges. Slithering between her breasts was a large snake curving up around one, and down between the other. The snake’s tongue licking toward the cunt, so open, so red in the lamp light. Hot and confused, the man walked back to his room, and with great difficulty, managed to fall asleep. The next morning, over strawberries, the woman asks him to stay another night. Again, he couldn’t sleep […]”

When I was 23, Lynn, the girl I was dating from film class, surprised me by taking me to watch erotica short films on Valentine’s Day. The event took place at The Mayfair Theater, an independent old movie theater. The architecture of the theater recalled North American Nickelodeons, but with a campy touch. Its balconies were decorated with life-size cardboard cutouts of Swamp Thing and Aliens.
That year, the festival was judged by adult star Kacie May and the program consisted of an hour and a half of short films. The content ranged from soft-core machismo-ridden shorts to scat fetish films. We watched a few minutes of what seemed to be heterosexual soft porn. It followed a couple who start making love in a modern living room space, then move to the bedroom. It was mostly footage of them kissing each other, touching each other, and making love missionary-style. Then a woman with a short brown bob crawled onto the bed, licking the back of her own hand in short strokes. She meowed and crawled over the unconcerned couple. They continued to make love. She crawled out to the kitchen, picked up her empty bowl with her teeth, and placed it onto a pillow. She kept walking over them until the end of the short. It seemed quite absurd. I began to laugh, but Lynn looked a bit uncomfortable. I then looked to our left, watching other audience members chugging beers and inhaling popcorn while laughing hysterically. Their uninterrupted laughter and loud comments really set the tone of the festival. Watching the audience became more interesting than watching the erotic films. The Mayfair Theater often showed cult films, and watching cult films is a communal experience.
It’s not exactly how I imagined my mother’s uncle watching porn in my grandfather’s theater. Movie theaters were openly screening porn films at that time, but I could not picture it happening within my mother’s hometown. I pictured him watching the film from the projector in the booth, so he could quickly stop the screening in case any unexpected guests decided to stop by. His friends sat on the balcony in the back. No one could get in from there unless they had a key, so it was safe. They had to think of everything. It was a conservative Christian neighborhood and they would not want to cause any trouble. They were most likely overcome with excitement and guilt. The voices of loud homoerotic banter merged with sound bites of grunting and moaning, but they reminded each other to keep it down every few minutes. They took turns to check the windows to make sure the sound was not loud enough to alarm any neighbors. Sometimes, they would turn off the speaker and there would be no sound.

After a political protest in 2019, I came across a bookstand on Riad El Solh street, close to Martyr’s Square in downtown Beirut. Towards the end of the table, past the copies of Hugo and de Beauvoir, I found a stack of erotica novels and adult magazines. They were all translations of Western publications. I really did not care which one I picked; I just knew I wanted to own a copy for the thrill of it. I looked for the most interesting cover art.
As he was giving me my change back, the vendor asked me, “Don’t I know you from somewhere?”
He scanned my breasts, gliding his eyes downwards. He probably assumed I worked in the porn or sex industry. I looked into his eyes and said, “No.” I turned around, ready to walk away with my magazine. He then stopped me to say that he had a large archive in his basement, and that he regularly sold porn collections and publications on EBay, to Europe and the USA. Although I was interested in rummaging through that archive, I was not comfortable enough to take his offer. It did not feel safe. I asked him where he found these novels. To my surprise, they were produced in Lebanon.
Walking towards the Riad El Solh statue, I read through the journal I had bought and found the format of the text somewhat canted; the font was a bit smudged, making it illegible. The photographs inside were comprised of faded pornographic collages. It looked raw; I liked that. The title of the novel read, Marcel’s Diaries.
The cover art was clearly a magazine cut-out pasted over a blue sheet. In the picture, a shirtless woman is grabbing her lover’s head, digging her fingers in his hair, while he is kissing her neck from behind. Her skirt is zipped down. Her lover has his hand on her lower right hip. She has her hand over his. Her lips are puckered up and open, almost like she is moaning with pleasure, her 1970s straight blonde hair running down her chest and partially covering her nipples.
I opened the first page. The preface read
which either translates to
“Desire
and deviance”
or to
“Desire
and kink”
I read through the first chapter and I found that whoever translated the text had changed the main character’s name to Fouad, an Arabic name. I assumed they wanted their Lebanese male audience to identify. As I read through, I found that all of his lovers had foreign names like Hanna, Marla, Marcel, Marta.


I realized on page 27, chapter four, that Marcel was one of Fouad’s lovers.

The scene took place in a movie theater. Movie theaters were often spaces for sexual freedom in North America, especially since the 1970s after the sexual revolution.
I also assumed they kept all the other foreign names so that it sounds exotic and less taboo. Pornography and erotica were attributed to West Hollywood, despite the fact that the Arab world historically produced erotic texts. Erotica became taboo, and the only way to safely produce it was to market it as foreign, as exotic.
It is interesting how the exotic covers for the erotic. The difference between the two adjectives is rooted in their Greek etymologies: exotic is from exo, “outside,” meaning alien or foreign. Erotic is derived from Eros, the god of sexual love. So, what’s exotic is mysterious and foreign – what’s erotic is sexy.
In Lebanon there is a thin line between the exotic and the erotic in cinema, like the thin line between art films and porn films. In 2015, during a conversation with filmmaker Jocelyne Saab in a Vietnamese restaurant in Paris, I learned that she had to shoot her art film Dunia a second time to change the dialect from Egyptian to Lebanese. She told me that her actors were Egyptian, and that she wasn’t strict about the script. She was not allowed to use Egyptian dialect. It had to be in Lebanese because the producers were concerned about the borderline erotic scenes in the film. So, they made it foreign.


L’enquête WITM mondiale est un des piliers essentiels de la troisième édition de notre recherche orientée sur l’action, intitulée Où est l’argent pour l’organisation des mouvements féministes? (abrégé en Où est l’argent ou WITM, pour l’acronyme en anglais). Les résultats de l’enquête seront développés et approfondis à l’occasion de conversations profondes avec des activistes et des financeurs, et les références seront croisées avec d’autres analyses et études existantes sur la situation du financement des mouvements féministes et de l’égalité des genres à travers le monde.
Le rapport complet de la recherche Où est l’argent pour l’organisation des mouvements féministes sera publié en 2026.
 Pour en apprendre davantage sur la manière dont l’AWID met en lumière l’argent utilisé pour et contre les mouvements féministes, consultez notre dossier WITM et nos précédents rapports à ce sujet ici.
Pour en apprendre davantage sur la manière dont l’AWID met en lumière l’argent utilisé pour et contre les mouvements féministes, consultez notre dossier WITM et nos précédents rapports à ce sujet ici.

 |
Tshegofatso Senne es unx feminista queer negrx con una enfermedad crónica. Buena parte parte de su trabajo se inscribe en el placer, la comunidad y los sueños, para el que se nutre del abolicionismo somático y la discapacidad, la sanación y las justicias transformadoras. Escribiendo, investigando y expresándose sobre cuestiones concernientes al feminismo, la comunidad, la justicia sexual y reproductiva, el consentimiento, la cultura de la violación y la justicia, Tshegofatso ha adquirido ocho años de experiencia teorizando sobre la intersección de estos tópicos con el placer. Tiene su propia actividad comercial, Thembekile Stationery, y la plataforma comunitaria Hedone, un espacio de reunión para analizar y comprender el poder de la toma de conciencia del trauma y el placer en la vida cotidiana. Tshegofatso trabaja con jóvenes de todo el continente, organiza talleres, presta asesoramiento en cuestiones de placer y liberación, y usa la creatividad y la narración como soluciones fractales a las injusticias sociales. |

En el cuerpo, no en el cerebro pensante, es donde experimentamos la mayoría de nuestro dolor, placer y alegría y donde procesamos la mayoría de lo que nos pasa. Es también donde realizamos la mayor parte de nuestra sanación, incluyendo nuestra sanación emocional y psicológica. Y es donde experimentamos la resiliencia y una sensación de fluidez.
Estas palabras, escritas por Resmaa Menakem en su libro My Grandmother’s Hands [Las manos de mi abuela], se han quedado conmigo.
El cuerpo alberga nuestras experiencias. Nuestras memorias. Nuestra resiliencia. Y como ha escrito Menakem, el cuerpo también alberga nuestros traumas. Responde con mecanismos de protección espontáneos para detener o evitar más daños. El poder del cuerpo. El trauma no es el evento mismo; es cómo responden nuestros cuerpos a los eventos que sentimos como peligrosos. A menudo queda atravesado en el cuerpo, hasta que lo abordamos. No se puede convencer a nuestro cuerpo de que no responda, simplemente lo hace.
Utilizando Digital Superpower, la aplicación de Ling Tan, fui registrando cómo se sentía mi cuerpo mientras recorría diferentes partes de mi ciudad, Johannesburgo, Sudáfrica. La aplicación es una plataforma guiada por gestos que te permite registrar tus percepciones mientras te mueves a través de diferentes lugares, cargando y grabando los datos. Yo la usé para registrar mis síntomas psicosomáticos (reacciones físicas conectadas a una causa mental). Podían ser flashbacks. Ataques de pánico. Opresión en el pecho. Un ritmo cardíaco rápido. Dolores de cabeza tensionales. Dolor muscular. Insomnio. Dificultad para respirar. Registré estos síntomas mientras caminaba y recorría distintas partes de Johannesburgo. Y me pregunté.
¿Dónde podemos estar segurxs? ¿Podemos estar segurxs?
Las respuestas psicosomáticas pueden ser causadas por una cantidad de cosas, y algunas no son tan severas como otras. Después de vivir cualquier tipo de trauma, puedes sentir un intenso malestar en eventos o situaciones parecidas. Registré mis sensaciones, ordenadas en una escala del 1 al 5, en la que el 1 representaba las instancias en las que apenas sentí alguno de estos síntomas – me sentía más cómoda que en guardia o nerviosa, mi respiración y mi ritmo cardíaco eran estables, no estaba mirando sobre mi hombro – y el 5 era lo opuesto: los síntomas me tenían cerca del ataque de pánico.
Como persona negra. Como persona queer. Como persona de género queer que puede ser percibida como mujer, dependiendo de cuál sea mi expresión de género ese día.
Me pregunté.
¿Dónde podemos estar segurxs?
Incluso en barrios que se podrían considerar «seguros», me he sentido constantemente en pánico. Mirando alrededor mío para asegurarme de que no me estaban siguiendo, acomodándome la camiseta de manera que no se me noten tanto los pechos, mirando alrededor para asegurarme de encontrar numerosas rutas para salir del lugar en el que estaba si me sintiera en peligro. Un camino vacío provoca ansiedad. Uno atestado también lo hace. Estar en un Uber también. Caminar en un camino público también. Estar en mi departamento también. Y también lo hace recibir una entrega a domicilio en la puerta de entrada del edificio.
¿Podemos estar segurxs?
Pumla Dineo Gqola habla de la fábrica de miedo femenino. Puede o no resultarte familiar, pero si eres alguien socializadx como mujer, conocerás bien esta sensación. La sensación que te hace planificar cada paso que das, ya sea que vayas a trabajar, a la escuela, o simplemente a hacer algún trámite. La sensación de que tienes que fijarte cómo te vistes, cómo actúas, cómo hablas tanto en público como en privado. La sensación en la boca del estómago si tienes que viajar de noche, recibir una entrega a domicilio o tratar con cualquier persona que sigue socializado como hombre cis. Acosadx en la calle, siempre con la amenaza de la violencia. Nuestra existencia en cualquier espacio viene con un miedo innato.
El miedo es tanto un fenómeno individual como sociopolítico. A nivel individual, el miedo puede presentarse como parte de un sistema de alarma saludable y bien desarrollado [...] Cuando pensamos en el miedo, es importante sostener ideas tanto acerca de la experiencia emocional individual como de las maneras políticas en las cuales el miedo ha sido utilizado para el control en diferentes épocas.
- Pumla Dineo Gqola, en su libro Rape: A South African Nightmare [La violación, una pesadilla sudafricana]
Las mujeres, femmes y queers sudafricanxs sabemos que cada paso que damos afuera – pasos para hacer las cosas cotidianas: caminar a las tiendas, un taxi al trabajo, un Uber desde una fiesta – todos estos actos son una negociación con la violencia. Este miedo es parte del trauma. Para soportar el trauma que cargamos en nuestros cuerpos, desarrollamos respuestas para detectar el peligro: mirar las respuestas emocionales de aquellxs a nuestro alrededor, leer buscando la «simpatía». Estamos constantemente en guardia.
Día tras día. Año tras año. Vida tras vida. Generación tras generación.
Acerca del desafío adicional de este sistema de defensa aprendido, Bessel Van Der Kolk, autor de The Body Keeps Score [El cuerpo lleva la cuenta], dijo:
Es que perturba esta capacidad de leer a otrxs con precisión, dejando a lx sobreviviente de trauma menos capaz de detectar el peligro o más proclive a percibir erróneamente peligro donde no lo hay. Insume una tremenda cantidad de energía seguir funcionando mientras se carga con la memoria del terror y la vergüenza de la absoluta debilidad y vulnerabilidad.
Como ha dicho Resmaa Menakem, el trauma está en todo. Se infiltra en el aire que respiramos, el agua que tomamos, los alimentos que comemos. Está en el sistema que nos gobierna, en la institución que nos enseña y que también nos trauma y dentro de los contratos sociales que acordamos con lxs demás. Lo que es más importante, lo llevamos con nosotrxs a todos lados a donde vamos, en nuestros cuerpos, mientras nos agota y erosiona nuestra salud y felicidad. Llevamos esa verdad en nuestros cuerpos. Lo hemos hecho durante generaciones.
Así que, mientras camino por mi ciudad, ya sea en un área que es considerada «segura» o no, llevo los traumas de generaciones cuyas respuestas están integradas a mi cuerpo. Mi corazón palpita, se hace difícil respirar, mi pecho se tensa, porque mi cuerpo siente como si el trauma estuviera sucediendo en ese mismo momento. Vivo en hiper vigilancia. Hasta el punto en el que unx está demasiado en guardia como para poder disfrutar plenamente su vida, o demasiado adormecidx para absorber nuevas experiencias.
Para comenzar a sanar, debemos reconocer estas verdades.
Estas verdades que viven en nuestros cuerpos.
Este trauma es lo que nos impide a muchxs vivir las vidas que queremos. Pregunta a cualquier femme o persona queer cómo es para ellxs la seguridad y seguramente te darán ejemplos de tareas simples: ser capaz de simplemente vivir vidas alegres, sin la amenaza constante de la violencia.
Las sensaciones de seguridad, de comodidad y de facilidad, son espaciales. Cuando encarnamos nuestro trauma, afecta las formas en las que percibimos nuestra propia seguridad, afecta las maneras en las que interactuamos con el mundo y altera las maneras en las que somos capaces de experimentar y encarnar cualquier cosa placentera y alegre.
Tenemos que rehusarnos a esta pesada responsabilidad y luchar por un mundo seguro para todxs. Caminando heridxs, como estamos muchxs, somos luchadorxs. El patriarcado puede aterrorizarnos y brutalizarnos, pero no abandonaremos la lucha. Cada vez que salimos a la calle, desafiando el miedo de maneras espectaculares y aparentemente insignificantes, nos defendemos y hablamos en nuestro propio nombre.
- Pumla Dineo Gqola, en su libro Rape: A South African Nightmare [Violación, una pesadilla sudafricana]
¿Dónde podemos estar segurxs? ¿Cómo comenzamos a defendernos, no solo en el sentido físico, sino en sentido emocional, psicológico y espiritual?
«El trauma nos convierte a todxs en armas», dijo adrienne maree brown en una entrevista realizada por Justin Scott Campbell. Y su obra, Pleasure Activism [Activismo del placer], nos ofrece numerosas metodologías para sanar ese trauma y afianzarnos en la comprensión de que la sanación, la justicia y la liberación también pueden ser experiencias placenteras. Especialmente quienes estamos más marginadxs, quienes puede que hayamos sido criadxs para equiparar el sufrimiento con «El trabajo». El trabajo que nos hemos tomado tantxs como activistas, constructorxs de comunidades, aquellxs que atienden a lxs más marginadxs, El trabajo que luchamos por hacer, quemándonos y raramente cuidando nuestras mentes y cuerpos. La alternativa es hacernos más conscientes de nuestro trauma, capaces de identificar nuestras propias necesidades y encarnar eso profundamente. Ese encarnar significa simplemente que somos más capaces de experimentar el mundo a través de los sentidos y las sensaciones en nuestros cuerpos, reconociendo lo que nos dicen, en vez de suprimir e ignorar la información que nos están comunicando.
Estar en conversación constante con nuestro cuerpo vivo y sostener intencionalmente esas conversaciones nos conecta más profundamente con lo encarnado, nos permite hacer tangibles las emociones que sentimos cuando interactuamos con el mundo, amigarnos con nuestros cuerpos y entender todo lo que están tratando de enseñarnos. Cuando entendemos que el trauma y el encarnar están acoplados, podemos comenzar la sanación y acceder al placer más integralmente, saludablemente, y en nuestras vidas cotidianas sin vergüenza ni culpa. Podemos comenzar a acceder al placer como una herramienta para el cambio individual y social, aprovechando el poder de lo erótico, como lo describió Audre Lorde. Un poder que nos permite compartir la alegría a la que accedemos y que vivimos, ampliando nuestra capacidad para la felicidad y entendiendo que somos merecedorxs de ello, incluso con nuestro trauma.
Aprovechar el placer y la encarnación de lo erótico nos da la amplitud de estar deliberadamente vivxs, sintiéndonos afianzadxs y estables y entendiendo nuestros sistemas nerviosos. Nos permite entender y descargarnos del equipaje generacional que hemos estado acarreando sin darnos cuenta; podemos tener el poder que nos da el conocimiento de que incluso tan traumatizadxs como estamos, tan traumatizadxs como podríamos estar en el futuro, aún somos merecedorx de vidas placenteras y alegres, que podemos compartir ese poder con nuestra gente. Es el aspecto comunitario lo que está faltando en la forma en que nos cuidamos; el autocuidado no puede existir sin cuidado comunitario. Somos capaces de sentir una confianza, seguridad y poder internos más profundos en nosotrxs mismxs, especialmente de cara a traumas futuros que van a ser disparadores, sabiendo cómo tranquilizarnos y estabilizarnos. Todo este entendimiento nos lleva a un poder interior más profundo que tiene recursos para enfrentar cualquier desafío que surja en nuestro camino.
Como somos lxs que vivimos con profundos traumas generacionales, nos hemos vuelto desconfiadxs y quizás pensemos que somos incapaces de contener y acceder al poder que tenemos. En «Los usos de lo erótico: lo erótico como poder», Lorde nos enseña que lo erótico nos ofrece una fuente de recarga, una forma de exigir lo mejor para nosotrxs y para nuestras vidas.
Porque lo erótico no es solo se trata de lo que hacemos, es una cuestión de con cuánta intensidad y plenitud podemos sentirnos mientras lo hacemos. Una vez que sabemos en qué medida somos capaces de sentir esa sensación de satisfacción y completitud, podemos observar cuál de nuestros diversos esfuerzos vitales nos lleva más cerca de esa plenitud.

No digo nada de esto livianamente, sé que es más fácil decirlo que hacerlo. Sé que muchxs de nosotrxs estamos impedidxs de entender estas verdades, de internalizarlas o incluso de sanarlas. La resistencia viene con momentos de inseguridad, pero no es imposible. Resistir las estructuras de poder que mantienen a salvo a lxs más poderosxs siempre pondrá en peligro a quienes fuimos empujadxs a los márgenes. Reconocer los traumas que has enfrentado es una recuperación de tus experiencias vividas, las que han pasado y las que vendrán; es la resistencia la que encarna el conocimiento de que somos merecedorxs de algo más que las migajas que estos sistemas nos han obligado a engullir. Es una resistencia que entiende que el placer es complicado por el trauma, pero que se puede acceder a él de formas arbitrarias y poderosas. Es una resistencia que reconoce que nuestro trauma es un recurso que nos conecta entre nosotrxs y que nos puede permitir mantenernos mutuamente a salvo. Es una resistencia que entiende que incluso con el placer y la alegría esto no es una utopía; aún causaremos y recibiremos daño, pero estaremos mejor equipadxs para sobrevivir y prosperar en una comunidad de cuidados diversos y amabilidad. Una resistencia que da paso a la sanación y la conexión con nuestro ser plenamente humanxs.
Sanar nunca será un recorrido fácil y optimista, pero comienza con el reconocimiento de la posibilidad. Cuando la opresión nos hace creer que el placer no es algo a lo que todxs podamos tener igual acceso, una de las maneras en las que comenzamos a hacer el trabajo de reclamar nuestro ser pleno – nuestro ser completo y liberado – es reclamando nuestro acceso al placer.
En su artículo en Pleasure Activism (con el cual ha contribuido), Leah Lakshmi Piepzna-Samarasinha ha dicho:
Sé que para la mayoría de la gente las palabras «cuidado» y «placer» ni siquiera pueden estar en la misma oración. Todxs estamos empapadxs en un odio capacitista hacia los cuerpos que tienen necesidades, y nos dan una opción realmente de mierda: o no tener necesidades para conseguir tener autonomía, dignidad y control sobre nuestra vida o admitir que necesitas cuidado y perder todo lo anterior.
¿Qué poder tiene esto? Entendemos nuestros traumas, de este modo, entendemos los de otrxs; encarnamos las sensaciones que experimentamos y vamos hacia ellas en vez de distraernos y evitarlas. Accedemos al placer de maneras que nos hacen querer compartir esa alegría con quienes son nuestra comunidad. Cuando tenemos conciencia del trauma, nos damos más lugar para experimentar todo esto y nos damos, a nosotrxs y a otrxs, el permiso para sanar. Imagina una comunidad en la cual todxs tienen acceso, recursos y tiempo para vivir vidas placenteras, en la forma que sea que quieran y merezcan; en la cual los traumas territoriales están mitigados porque las personas que los ocupan son conscientes del trauma y están llenas de cuidado tierno. ¿No es eso sanador? ¿No es eso trabajar los traumas generacionales? ¿No construye y sostiene eso futuros más sanos para todxs?
Es tiempo de que reconectemos con el conocimiento ancestral de que merecemos vivir vidas plenas. Necesitamos volver a estar en contacto con nuestro derecho natural a la alegría y a existir para nosotrxs. A sentir placer simplemente por el hecho de sentirlo. A no vivir vidas de terror. Suena radical, se siente radical. En un mundo donde hemos sido socializadxs y traumatizadxs para el entumecimiento, para el miedo, para sentirnos y seguir estando impotentes, para ser codiciosxs y vivir con temas estructurales que nos llevan a la enfermedad mental, qué regalo y qué maravilla es empezar a sentir, a estar en comunidad con quienes sienten, a ser sanamente interdependientes, a amarnos mutuamente. Sentir es radical. El placer es radical. Sanar es radical.
Tienes permiso para sentir placer. Tienes permiso para bailar, crear, hacerte el amor a ti mismx y a otrxs, celebrar y cultivar la alegría. Te aliento a que lo hagas. Tienes permiso para sanar. No te lo guardes dentro, no intentes atravesar este momento solx. Tienes permiso para hacer el duelo. Y tienes permiso para vivir.
- adrienne maree brown, «You Have Permission» [Tienes permiso]
La encarnación somática nos permite explorar nuestro trauma, trabajarlo y establecer conexiones significativas con nosotrxs mismxs y con el colectivo. Hacer esto a lo largo del tiempo sostiene nuestra sanación; al igual que el trauma, la sanación no es un evento de una única vez. Esta sanación nos ayuda a avanzar hacia la liberación individual y colectiva.
En «A Queer Politics of Pleasure» [Una política queer del placer], Andy Johson habla acerca de las formas en las que hacer que el placer sea queer nos ofrece fuentes de sanación, aceptación, liberación, juego, plenitud, desafío, subversión y libertad. ¡Qué amplio! Cuando encarnamos el placer en formas que son tan integrales, tan queer, somos capaces de reconocer la limitación.
Hacer que el placer sea queer también nos plantea las preguntas que entrecruzan nuestros sueños con nuestras realidades de vida.
¿Quién es libre o consideradx suficientemente valiosx para sentir placer? ¿Cuándo se tiene permitido sentir placer o satisfacción? ¿Con quién se puede sentir placer? ¿Qué clase de placer es accesible? ¿Qué nos limita para acceder a todo nuestro potencial erótico y de satisfacción?
- Andy Johnson, «A Queer Politics of Pleasure» [Una política queer del placer]
Cuando nuestras prácticas de placer conscientes del trauma están basadas en el cuidado comunitario, comenzamos a responder algunas de estas preguntas. Comenzamos a entender el potencial liberador. Como activistas del placer, esta es la realidad en la que nos afirmamos. La realidad que dice: mi placer puede ser fractal, pero tiene el potencial de sanarme no solo a mí y a mi comunidad, sino a futuros linajes.
Soy un sistema entero; somos sistemas enteros. No somos solo nuestros dolores, solo nuestros miedos ni solo nuestros pensamientos. Somos sistemas enteros preparados para el placer y podemos aprender cómo decir sí desde adentro.
- Prentis Hemphill, entrevistadx por Shar Jossell
Hay un mundo de placer que nos permite comenzar a entendernos integralmente, de formas que nos dejen lugar para reconstruir las realidades que afirman que somos capaces y merecedorxs de placer cotidiano. El BDSM, uno de mis placeres más profundos, me permite dar un vistazo a estas realidades en las que puedo tanto sentir como sanar mi trauma, así como sentir innumerables oportunidades para decir sí desde adentro. Mientras que el trauma me mantiene estancada en un ciclo de luchar o huir, el bondage , el estar de rodillas, el impacto y el juego de asfixia me alientan a mantenerme en tierra y conectadx, reconectando con la reparación. El placer que es lúdico me permite sanar, identificar dónde está guardada en mi cuerpo la energía traumática y enfocarla ahí. Me permite expresar las sensaciones que siente mi cuerpo a través de gritos de dolor y de placer, expresar mi no sin miedo y deleitarme en el puto sí. Con un plan de seguridad, cuidado posterior y una comprensión profunda del trauma, lo retorcido ofrece un lugar para el placer y la sanación que es invaluable.
Así que tanto si tu placer es cocinar una comida a tu gusto, tener sexo, pasar el día en la cama con tu gente, participar en colectivos de cuidado de personas con discapacidad, que alguien te escupa en la boca, ir a excursiones accesibles, tener citas tiernas, asistir a una fiesta bailable en línea, dedicar tiempo a tu jardín, ser ahogadx en un calabozo, espero que lleves el placer contigo donde sea que vayas. Espero que te sane a ti y a tu gente.
Reconocer el poder de lo erótico en nuestras vidas puede darnos la energía para buscar un cambio genuino en nuestro mundo.
- Audre Lorde, «Uses of the Erotic: The Erotic as Power» [Los usos de lo erótico: lo erótico como poder]


Esta edición en alianza con Kohl: una publicación para Body and Gender Research analizará soluciones, propuestas y realidades feministas para transformar nuestro mundo actual, nuestros cuerpos y nuestras sexualidades.

نصدر النسخة هذه من المجلة بالشراكة مع «كحل: مجلة لأبحاث الجسد والجندر»، وسنستكشف عبرها الحلول والاقتراحات وأنواع الواقع النسوية لتغيير عالمنا الحالي وكذلك أجسادنا وجنسانياتنا.

