
Ronnie Gilbert

Over the past few years, a troubling new trend at the international human rights level is being observed, where discourses on ‘protecting the family’ are being employed to defend violations committed against family members, to bolster and justify impunity, and to restrict equal rights within and to family life.
The campaign to "Protect the Family" is driven by ultra-conservative efforts to impose "traditional" and patriarchal interpretations of the family, and to move rights out of the hands of family members and into the institution of ‘the family’.
Since 2014, a group of states have been operating as a bloc in human rights spaces under the name “Group of Friends of the Family”, and resolutions on “Protection of the Family” have been successfully passed every year since 2014.
This agenda has spread beyond the Human Rights Council. We have seen regressive language on “the family” being introduced at the Commission on the Status of Women, and attempts made to introduce it in negotiations on the Sustainable Development Goals.
AWID works with partners and allies to jointly resist “Protection of the Family” and other regressive agendas, and to uphold the universality of human rights.
In response to the increased influence of regressive actors in human rights spaces, AWID joined allies to form the Observatory on the Universality of Rights (OURs). OURs is a collaborative project that monitors, analyzes, and shares information on anti-rights initiatives like “Protection of the Family”.
Rights at Risk, the first OURs report, charts a map of the actors making up the global anti-rights lobby, identifies their key discourses and strategies, and the effect they are having on our human rights.
The report outlines “Protection of the Family” as an agenda that has fostered collaboration across a broad range of regressive actors at the UN. It describes it as: “a strategic framework that houses “multiple patriarchal and anti-rights positions, where the framework, in turn, aims to justify and institutionalize these positions.”

What if we perceived land and Nature not as private property to exploit, but as a whole to live in, learn from, and harmoniously coexist with? What if we repaired our relationships with the land and embraced more sustainable alternatives that nurture both the planet and its communities?
Nous Sommes la Solution (We Are the Solution, NSS) is one of many women-led movements striving to do this. This is their story.

Notre force collective, notre sagesse et notre engagement sont illimités... mais pas nos comptes en banque.
Cette synthèse s’appuie sur les réponses de 1 174 organisations féministes, de défense des droits des femmes, LBTQI+ et alliées (désignées ci-après comme « organisations féministes et de défense des droits des femmes ») issues de 128 pays, ayant participé à l’enquête Où est l’argent pour l’organisation des mouvements féministes ?. Les données reflètent les expériences vécues entre 2021 et 2023, et sont examinées au regard des tendances de restrictions budgétaires qui se profilent pour 2024–2025.
Découvrez l’état des lieux du financement des organisations féministes aujourd’hui.
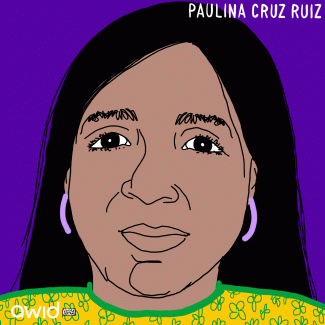
Paulina Cruz Ruiz, from the Rabinal, Baja Verapaz region of Guatemala, was an ancestral Maya Achí (Indigenous) authority and a human rights defender.
She was actively involved in community organizing and resistance, including legal measures against mining projects on Indigenous territory, projects that would severely affect and damage the socio-environmental fabric.
“The extractive industry model promoted by the Guatemalan government and the construction of large-scale development projects on indigenous lands without community consent has been a source of ongoing disputes with resistance movements.” - Minority Rights Group International
Paulina was also part of the March for Dignity, Life and Justice, in which on 1 May 2019 thousands of Guatemalans started a march of eight days against corruption and impunity in the prosecution and assassinations of human rights, peasant and Indigenous leaders and land defenders.
Paulina was murdered on 14 September 2019 near her home in the village of Xococ.
According to the Minority Rights Group International, “one of the major ongoing issues affecting Mayan communities is the increasing activity of the mining industry.”
Read more about the Mayans of Guatemala
Read more about the March for Dignity, Life and Justice
Priscilla has nearly two decades of experience working in the non-profit sector with social justice organizations that worked on women and youth rights, conservation, peacebuilding and development. Her interests are in setting up progressive processes and systems that will help an organization live to their values and principles and thrive, and finding ways to support organizations and fundraisers to locate and secure the resourcing they need to do good work. . Priscilla joined AWID in 2018 as Resource Mobilization Manager and in July 2023, took on the role of Director of Operations and Funding Partnerships.
Priscilla holds an MSc in International Politics from the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS), a growing pile of books she is still trying to find time to read, and sits on the Board of Hodan Somali Community, a London-based charity.

Là où les organisations de terrain pilotent et les multinationales sont tenues responsables.
📅 Mardi 11 novembre 2025
📍 En ligne et à l'Universidade Federal do Pará, Belém
Marta es une investigadore y activista queer transfeministe no binarie de la antigua Yugoslavia que, actualmente, reside en Barcelona. Trabaja como organizdore de movimientos transnacionales, economista feminista y constructore de sistemas alternativos. Es confundadore y une de les coordinadores de Global Tapestry of Alternatives, un proceso global que busca identificar, documentar y poner en contacto alternativas de tapicería en los ámbitos local, regional y mundial. En el plano local, participa en organizaciones transfeministas, queer, de personas migrantes y contra el racismo. Además, posee un doctorado en Ciencias Ambientales y Tecnología de la Universidad Autónoma de Barcelona, centrado en las perspectivas feministas decoloniales de un pluriverso de alternativas sistémicas y la creación de sistemas alternativos feministas, basados en el cuidado y la sostenibilidad de la vida. En sus ratos libres, disfruta del boxeo, tocar la guitarra y la batería como integrante de una banda de samba, también se recrea en la fotografía, el senderismo, en cocinar para sus afectos y malcriar a sus dos gatos.
Nous Sommes la Solution eleva y multiplica el liderazgo de las mujeres rurales que trabajan por soluciones realmente africanas para la soberanía alimentaria.

*Website in French
Elina est une jeune avocate des droits humains afro-dominicaine et féministe intersectionnelle, engagée à utiliser sa voix et ses compétences pour construire un monde plus juste, empathique et inclusif. Elle a commencé la faculté de droit à 16 ans, convaincue que cela lui donnerait les outils nécessaires pour comprendre et promouvoir la justice sociale. Après un JD (doctorat en droit) en République dominicaine, elle a poursuivi un LL.M. (maîtrise en droit) en droit international public et droits humains au Royaume-Uni en tant que boursière Chevening. Seule femme latino-caribéenne de sa classe, elle a obtenu son diplôme avec distinction.
Elina a travaillé à l'intersection des droits humains, du genre, de la migration et de la politique et ceci à plusieurs niveaux : des instances étatiques aux collectifs de base aux organisations internationales. Elle a aidé à plaider des cas de violence sexiste devant la Cour interaméricaine des droits de l'homme. En tant que membre du Groupe consultatif des jeunes du FNUAP, elle a contribué au renforcement des droits sexuels et reproductifs en République dominicaine. Elle a codirigé la première campagne d'Amnesty International sur les droits des travailleur.euse.s du sexe dans les Amériques, développant des partenariats solides avec des organisations dirigées par des travailleur.euse.s du sexe et utilisant la position d'Amnesty pour amplifier la voix des femmes défenseurs des droits humains et des travailleur.euse.s du sexe. Elina fait partie de Foro Feminista Magaly Pineda et de la Global Shapers Community. Elle parle espagnol, français et anglais.
Grâce à la richesse de son expérience, Elina apporte à l’AWID de solides compétences de gouvernance et de planification stratégique et un savoir-faire éprouvé en matière de mécanismes des Nations Unies et des droits humains régionaux. Elle affirme également très clairement sa détermination à continuer de faire de l’AWID une organisation inclusive pour toutes les femmes, et particulièrement les jeunes féministes et celles des Caraïbes. C’est avec la diversité de ces apports qu’Elina rejoint une sororité de féministes internationales qui ont du mordant. Elle pourra continuer à y développer son leadership féministe, pour ne plus jamais se sentir seule dans cette voie.
Coopérative Textile Nadia Echazú

A hands-on deckgame for collectives to explore feminist economic alternatives and systems of care as crisis response. This deckgame is for all movements navigating global climate crises through play and strategy based on real-life scenarios. A creative avenue to strategize in meetings, workshops, and community gatherings!
Maria is a graphic designer and visual communicator. Maria has worked with NGOs and Human Rights like Profamilia and OXFAM. As a woman of the Global South, she feels especially called to use her skills to work with organizations that help protect the wellbeing, as well the rights of millions of girls and women in Latin America.

1 of 3 trans and travesti people in Argentina live in a poor household

Suivez la campagne:
Rejoignez-nous
Devenir membre| Rejoignez notre communauté
Ne ratez rien des actualités
Abonnez-vous pour les actualités
Des questions ?
Contactez : communications @ awid.org